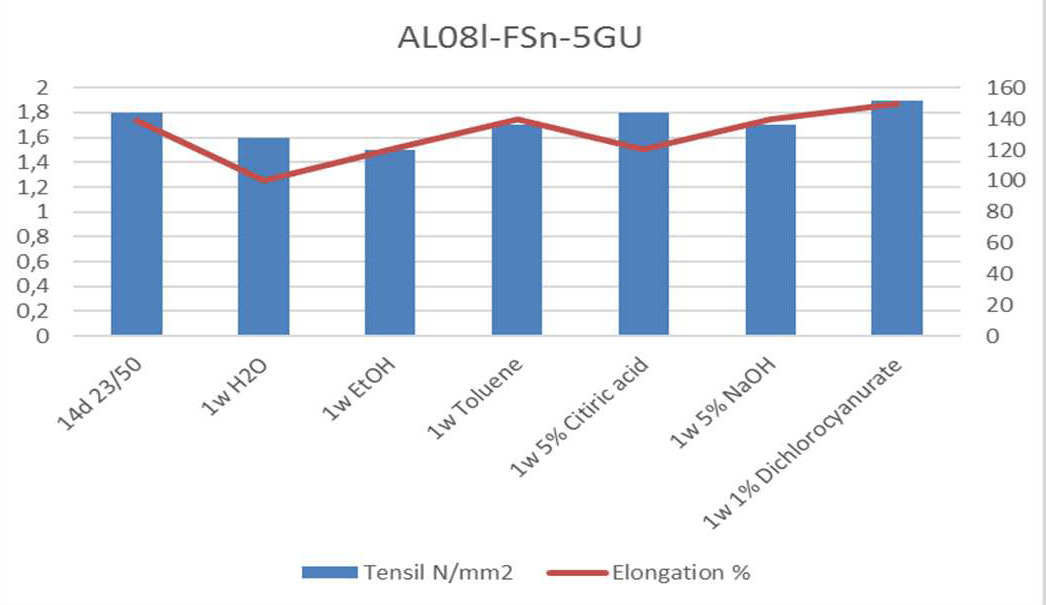
What makes “SilaCote” “Chemical Resistant”?
Using a particular bend additives and pure Silane silicone materials used in “SilaCote” has proven outstanding chemical resistance ph2 - ph13. The high chemical resistance of the raw materials used in combined with high cross linking of the moisture triggered technology makes a very chemical resistant product. The success of SilaCote systems used are proven in chemically harsh environments like in the waste water-, chemical, petrochemical and pulp- and paper industry.
Silanes are an integral component of modern coatings.
The particular role which they are called on to play in the formulation of coatings and their modification of binders depends on their individual chemical structure.
There are essentially two ways to incorporate them into coatings. The first is to use them as an additive for the binder or for the finished coating formulation while the second is to chemically integrate them into the binder by means of an addition-polymerization, copolymerization or grafting reaction. Silanes also serve as feedstocks for numerous industrial processes, which yield coatings that are very thin, yet extremely durable.
Silanes as Adhesion Promoters -
Organofunctional silanes promote the adhesion of many types of coatings to a wide variety of substrates. An organofunctional silane is a hybrid compound that combines the inorganic functionality of an alkyl silicate, with the functionality of a reactive organic group – all in a single molecule. The inorganic functionality of the silane reacts with the different OH groups present in the fillers or polymers.
This is a two step process, in which the alkoxy group (usually methoxy or ethoxy)is first hydrolyzed. In the subsequent step, after the alcohol is released, the silanol groups thus obtained react with available OH groups.
INDUSTRIAL COATINGS I SILanes
CREATING TOMORROW’S SOLUTIONS
SILANES FOR COATINGS APPLICATIONS
The organic portion of the silane is usually compatible with, or reactive towards, the binder incorporated in the coating. This hybrid character - inorganic and organic – that silanes exhibit allows them to act as a ‘bridge’ between two dissimilar materials.
By establishing a chemical bond at the interface with the substrate, and attaching themselves to suitable chain ends in the coating binder, silanes increase the adhesion of the coating binder to the substrate,creating stronger adhesive bonding that can even withstand extreme loads. In practical use, the silane in this case SilaCote is admixed with the formulated coating, it can be applied as a separate prime coat formulation if required.
Advantages of organic and organofunctional silanes
• Wide selection of organosilanes for gel processes
• High-quality organofunctional silanes
• Alpha-silanes allow for new formulating scope
At a Glance Silanes as Crosslinkers Organofunctional silanes are capable of reacting at room temperature with complementary chemical groups on different polymers which make up the different coating binders (e.g. hydroxyl, epoxy, carboxyl, acrylic). This capability is exploited in numerous applications, including room temperature- curing sealants, high chemical resistant coatings, polysiloxane topcoats and fouling-release coatings for ships.